how_to_check marginal mandibular nerve
In this article, we will delve into the intricate process of checking the marginal mandibular nerve. The marginal mandibular nerve is a vital component of the human anatomy, responsible for various functions in the lower face. Understanding this nerve and how to assess its condition is crucial for healthcare professionals who specialize in otolaryngology and maxillofacial surgery.
Understanding the Marginal Mandibular Nerve
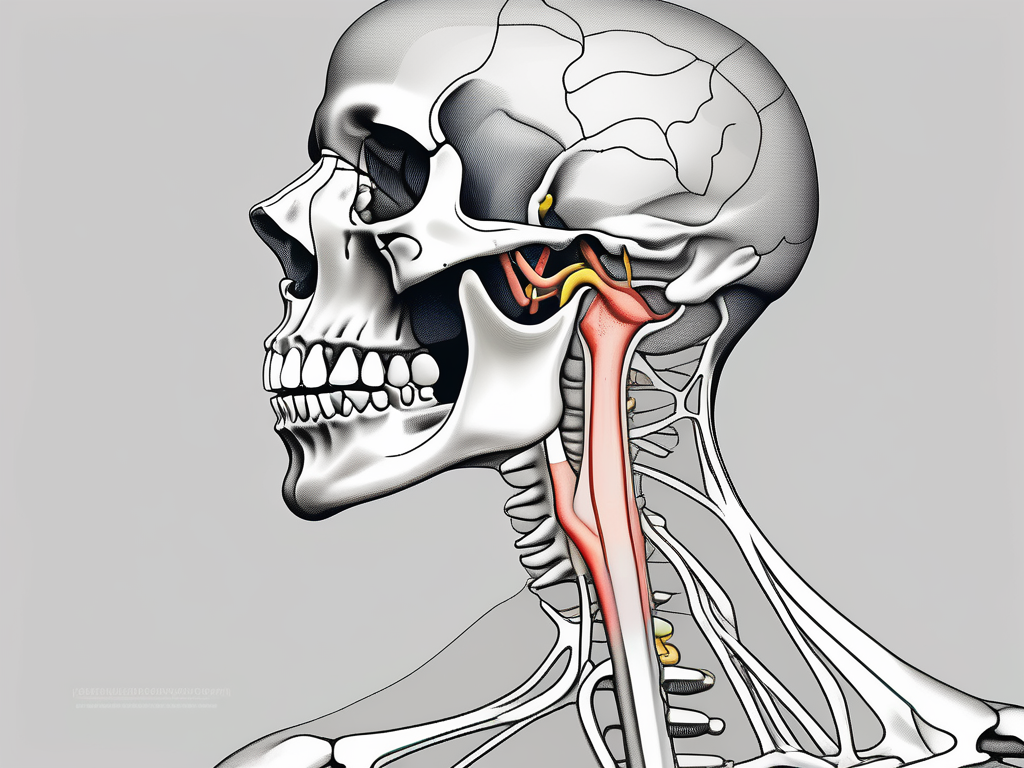
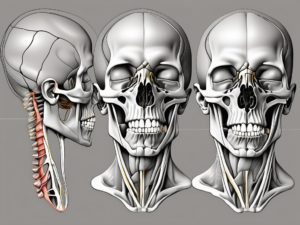
The marginal mandibular nerve is a branch of the facial nerve that plays a substantial role in the motor control of the lower lip and chin. This nerve travels in close proximity to the lower margin of the mandible and is susceptible to injury during certain surgical procedures or trauma. By familiarizing ourselves with the anatomy and functions of the marginal mandibular nerve, we can ensure accurate assessments and provide proper care to our patients.
Anatomy of the Marginal Mandibular Nerve
The marginal mandibular nerve originates from the facial nerve within the parotid gland. It descends along the mandible’s lower margin, passing deep to the platysma muscle and ending at the lower lip. Knowledge of the nerve’s trajectory and its relation to surrounding structures is essential to avoid accidental damage during surgical interventions or when addressing trauma to the lower face.
The parotid gland, where the marginal mandibular nerve originates, is the largest of the salivary glands. It is located in front of the ear and extends downward to the angle of the mandible. The gland produces saliva, which aids in the digestion of food and helps maintain oral health. The proximity of the marginal mandibular nerve to this important gland highlights the need for careful surgical planning and precision to avoid potential complications.
As the marginal mandibular nerve descends along the lower margin of the mandible, it passes deep to the platysma muscle. The platysma is a thin, broad muscle that covers the front of the neck. It helps to lower the jaw and lip, contributing to facial expressions such as frowning or grimacing. The close relationship between the marginal mandibular nerve and the platysma muscle underscores the importance of understanding the nerve’s anatomy to preserve its function during surgical procedures.
Functions of the Marginal Mandibular Nerve
The main role of the marginal mandibular nerve is to provide motor innervation to the muscles of the lower lip and chin. Dysfunction or damage to this nerve can lead to asymmetry or weakness in these areas, adversely affecting a patient’s facial expression and speech. Assessing the nerve’s function is crucial for diagnosing potential nerve injury and developing appropriate treatment plans.
The muscles innervated by the marginal mandibular nerve include the depressor labii inferioris, depressor anguli oris, and mentalis muscles. The depressor labii inferioris muscle lowers the lower lip, while the depressor anguli oris muscle pulls down the corner of the mouth, contributing to expressions such as a frown or a grimace. The mentalis muscle, located in the chin area, helps to elevate and protrude the lower lip. These muscles work together to allow for various facial expressions and proper speech articulation.
Understanding the functions of the marginal mandibular nerve is essential not only for surgeons and healthcare professionals but also for patients. Being aware of the potential impact of nerve injury can help patients make informed decisions about their treatment options and recovery expectations. Rehabilitation techniques, such as physical therapy or speech therapy, may be necessary to restore optimal function and improve quality of life for individuals affected by marginal mandibular nerve dysfunction.
Preparing for the Examination
Prior to conducting a thorough examination of the marginal mandibular nerve, it is imperative to ensure that you have the necessary equipment and that your patient is adequately prepared.
Necessary Equipment for Checking the Nerve
To assess the marginal mandibular nerve accurately, you will require specific tools. These include a bright light source, blunt-tipped forceps, cotton swabs, a mirror, and a medical-grade measuring tape. Having these items readily available will facilitate a smooth examination process.
Let’s take a closer look at each of these tools:
A bright light source is essential for illuminating the area where the marginal mandibular nerve is located. This will help you clearly visualize the nerve and any abnormalities that may be present.
Blunt-tipped forceps are used to gently manipulate the tissues surrounding the nerve. These forceps allow for precise movements without causing any damage or discomfort to the patient.
Cotton swabs are useful for applying pressure to specific points along the nerve pathway. This can help you assess the patient’s sensitivity and identify any areas of heightened or diminished sensation.
A mirror is a valuable tool for examining the nerve from different angles. It allows you to view areas that may be difficult to see directly, providing a comprehensive assessment of the nerve’s condition.
A medical-grade measuring tape is used to accurately measure the distance between specific landmarks on the patient’s face. This measurement can help determine the exact location of the nerve and guide your examination process.
Patient Preparation Guidelines
Before commencing the examination, it is crucial to provide your patient with comprehensive guidance on what to expect. Explain the procedure clearly, addressing any concerns they might have. Obtain their informed consent and ensure their comfort throughout the examination. Remember, communication is key when working with patients, and assisting them in understanding the process can alleviate anxiety and foster trust.
Here are some additional tips for preparing your patient:
1. Create a calm and welcoming environment in the examination room. Ensure that the lighting is comfortable and the temperature is appropriate for the patient’s comfort.
2. Offer the patient a comfortable chair or reclining position to help them relax during the examination. This will also allow you to have better access to the nerve area.
3. Provide the patient with a detailed explanation of the examination procedure, including the purpose, potential sensations they may experience, and any possible risks or complications. Encourage them to ask questions and address any concerns they may have.
4. Obtain the patient’s informed consent before proceeding with the examination. This ensures that they are fully aware of the procedure and have given their permission for you to proceed.
5. Throughout the examination, regularly check in with the patient to ensure their comfort. Ask if they are experiencing any pain or discomfort and make adjustments as necessary.
By following these guidelines and ensuring that you have the necessary equipment, you can effectively prepare both yourself and your patient for a thorough examination of the marginal mandibular nerve. Remember, a well-prepared patient and a well-equipped examiner contribute to a successful examination process.
Procedure for Checking the Marginal Mandibular Nerve
Now that we have discussed the essential preparatory steps, let us delve into the comprehensive procedure for assessing the marginal mandibular nerve.
The examination of the marginal mandibular nerve involves a systematic approach to ensure a thorough assessment. The following steps provide a structured framework:
- Cleanse and disinfect your hands thoroughly.
- Ensure proper lighting in the examination room to aid visualization.
- Gently palpate the submandibular triangle to locate and mark the course of the marginal mandibular nerve.
- Compare the mobility, symmetry, and strength of the lower lip and chin muscles bilaterally.
- Perform a detailed visual assessment of the lower lip, noting any asymmetry or abnormalities.
- Using blunt-tipped forceps, tactfully stimulate the marginal mandibular nerve bilaterally to assess the patient’s response.
- Record any findings accurately, paying particular attention to the quality of muscle movement, strength, and response to stimulation.
When palpating the submandibular triangle, it is important to apply gentle pressure to avoid causing discomfort to the patient. By carefully locating and marking the course of the marginal mandibular nerve, you can ensure accurate assessment and avoid any unnecessary complications.
Assessing the mobility, symmetry, and strength of the lower lip and chin muscles is crucial in evaluating the function of the marginal mandibular nerve. By comparing both sides of the face, you can identify any discrepancies or abnormalities that may indicate nerve dysfunction.
A visual assessment of the lower lip provides valuable information about the overall appearance and function of the marginal mandibular nerve. Look for any signs of asymmetry, such as drooping or unevenness, as well as any abnormalities that may affect the nerve’s performance.
Stimulating the marginal mandibular nerve with blunt-tipped forceps allows for a direct evaluation of the nerve’s sensitivity and responsiveness. By applying gentle pressure to the nerve bilaterally, you can observe the patient’s reaction and determine if there are any issues with nerve conduction.
Accurate documentation of your findings is essential for proper diagnosis and treatment planning. When recording your observations, be sure to describe the quality of muscle movement, the strength of the muscles involved, and the patient’s response to stimulation. This detailed information will assist in formulating an effective management plan.
Safety Measures During the Procedure
Throughout the examination, it is crucial to maintain a sterile environment and adhere to strict infection control protocols. Ensure that all instruments are properly sterilized, and dispose of any single-use items appropriately. Additionally, make certain the patient is comfortable, and monitor their well-being during the procedure.
Creating a safe and comfortable environment for the patient is paramount during the assessment of the marginal mandibular nerve. By following proper infection control protocols and maintaining a sterile environment, you minimize the risk of complications and promote patient safety. Regularly checking on the patient’s well-being throughout the procedure ensures their comfort and allows for immediate intervention if necessary.
Interpreting the Results
Interpreting the examination results is paramount to understanding the condition of the marginal mandibular nerve and formulating an appropriate course of action.
The examination of the marginal mandibular nerve involves assessing the movement of the lower lip and chin muscles, as well as the responses to stimulation. By carefully analyzing these findings, healthcare professionals can gain valuable insights into the functionality of the nerve and make informed decisions regarding patient care.
Normal Findings and What They Mean
A normal examination would reveal symmetrical, effortless movement of the lower lip and chin muscles, with appropriate responses to stimulation. These findings indicate that the marginal mandibular nerve is functioning optimally, providing reassuring results for both the healthcare professional and patient.
When the lower lip and chin muscles move in a coordinated and symmetrical manner, it suggests that the nerve is transmitting signals effectively. This smooth movement allows for normal speech, eating, and facial expressions, contributing to an overall sense of well-being.
Furthermore, the appropriate responses to stimulation indicate that the nerve is capable of detecting and reacting to external stimuli. This responsiveness is crucial for maintaining the integrity of the nerve and ensuring its proper functioning in various situations.
Abnormal Findings and Potential Causes
In cases where asymmetry, weakness, or a lack of response is observed, the marginal mandibular nerve’s functionality may be compromised. These abnormal findings raise concerns and require further investigation to determine the underlying cause.
One potential cause for abnormal findings is nerve compression. When the nerve is compressed or squeezed, its ability to transmit signals may be hindered, resulting in impaired movement and responsiveness. Nerve compression can occur due to various factors, such as tumors, cysts, or inflammation in the surrounding tissues.
Trauma to the marginal mandibular nerve can also lead to abnormal examination results. Injuries, such as facial fractures or lacerations, can damage the nerve and disrupt its normal functioning. The severity of the trauma and the extent of the nerve damage will influence the nature and severity of the abnormalities observed during the examination.
Additionally, previous surgical interventions in the area of the marginal mandibular nerve can contribute to abnormal findings. Surgical procedures, such as facelifts or reconstructive surgeries, may inadvertently affect the nerve, resulting in altered movement and responsiveness. It is crucial to consider the patient’s medical history and any prior surgical procedures when interpreting the examination results.
When abnormal findings are detected during the examination, it is essential to consult with a specialist in nerve disorders. These specialists have the expertise to further investigate the deviations and formulate an appropriate management plan. The specific course of action will depend on the underlying cause of the abnormalities and may involve further diagnostic tests, medication, physical therapy, or surgical interventions.
By thoroughly interpreting the examination results and considering potential causes for abnormal findings, healthcare professionals can provide comprehensive care to patients with marginal mandibular nerve issues. Early detection and appropriate management are crucial for optimizing patient outcomes and improving their quality of life.
Post-Examination Procedures
Once the examination is complete and the results have been interpreted, certain crucial steps should be undertaken to ensure that both the patient and healthcare professional are well-informed and prepared for the next stages of care.
Communicating the Results to the Patient
Effectively conveying the findings of the examination is vital for patient comprehension and engagement. Clearly explain the results, providing information on any abnormalities and potential causes. It is vital to emphasize the importance of seeking further guidance from a specialist to develop an appropriate treatment plan specific to their condition.
Possible Follow-Up Procedures
Depending on the examination findings, certain follow-up procedures may be necessary. These can include further diagnostic tests, consultations with specialists in neurology or maxillofacial surgery, or possible surgical interventions. Collaboration with an interdisciplinary team can optimize patient care and ensure the most suitable treatment strategies are implemented.
Complications and Risks
Although the examination of the marginal mandibular nerve is generally safe, healthcare professionals must be aware of potential complications and risks.
Potential Risks of the Examination
There is a minimal risk of infection or minor discomfort during the examination process. However, these risks can be minimized by adhering to strict aseptic techniques, following proper sterilization protocols, and ensuring patient comfort throughout the procedure.
How to Manage Complications
If any complications arise during the examination or subsequent procedures, it is crucial to promptly address them. Proper documentation of the complication, open communication with the patient, and collaboration with a specialist can help navigate these challenges effectively and ensure the best possible outcome for the patient.
Prevention and Care
Preventive measures and appropriate care are essential for maintaining the health and integrity of the marginal mandibular nerve.
Tips for Maintaining Nerve Health
While it is not possible to entirely prevent nerve damage or injury, various strategies can help minimize the risk. These include maintaining an overall healthy lifestyle, avoiding trauma to the lower face, and adhering to proper surgical techniques when operating in the region. Ensuring appropriate surgical training and continuous professional development can significantly contribute to the safety and success of procedures involving the marginal mandibular nerve.
Preventive Measures Against Nerve Damage
It is important to educate patients on potential sources of trauma to the lower face and encourage vigilance when engaging in activities that carry a risk of nerve injury. Advising patients on proper dental and oral hygiene practices can reduce the likelihood of infections or inflammation that might affect nerve function. Additionally, promoting the implementation of strict safety protocols in surgical settings can further minimize the potential for nerve damage.
In conclusion, understanding how to check the marginal mandibular nerve is crucial for healthcare professionals in otolaryngology and maxillofacial surgery. By comprehending the nerve’s anatomy, functions, and implementing a meticulous examination procedure, accurate assessments can be made. Interpreting the examination results, communicating them effectively, and providing appropriate post-examination care are vital components of patient management. By prioritizing safety, preventing complications, and emphasizing preventive measures, healthcare professionals can optimize patient care and contribute to the well-being of those relying on their expertise.