how to check marginal mandibular nerve
The marginal mandibular nerve is an important anatomical structure that plays a crucial role in the innervation of the lower lip and chin. By understanding its anatomy and function, healthcare professionals can effectively assess its integrity and ensure proper patient care. In this article, we will discuss the step-by-step procedure for checking the marginal mandibular nerve, as well as safety measures, interpreting results, and post-examination follow-up.
Understanding the Marginal Mandibular Nerve
Anatomy of the Marginal Mandibular Nerve
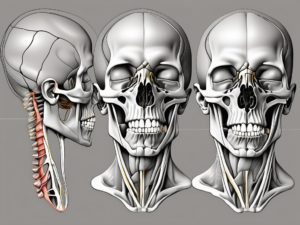
The marginal mandibular nerve is a branch of the facial nerve, specifically originating from the mandibular division, or V3 segment, of the trigeminal nerve. It travels along the anterior border of the lower jaw, obliquely crossing the inferior margin of the mandible, before branching out to supply the lower lip and chin. Its location and course can vary slightly among individuals, making a thorough understanding of its anatomy crucial for accurate examination.
When examining the anatomy of the marginal mandibular nerve, it is important to note that its path is not always consistent. Variations in its course can occur due to individual differences in facial structure. In some individuals, the nerve may take a more direct route, while in others, it may follow a slightly more circuitous path. These variations highlight the complexity of the facial nerve system and emphasize the need for careful examination and assessment.
As the marginal mandibular nerve travels along the anterior border of the lower jaw, it passes through various anatomical structures. It runs deep to the platysma muscle, a thin sheet of muscle that covers the front of the neck and extends to the lower face. The nerve then continues its course, crossing the inferior margin of the mandible. This crossing point is an important landmark for identifying the nerve during surgical procedures or diagnostic examinations.
Once the marginal mandibular nerve reaches the lower lip and chin, it branches out to supply the muscles responsible for their movements. The depressor anguli oris muscle, located at the corner of the mouth, is innervated by the nerve and plays a role in lowering the corners of the mouth. The depressor labii inferioris muscle, situated below the lower lip, is also supplied by the marginal mandibular nerve and aids in depressing the lower lip. Additionally, the mentalis muscle, which is responsible for chin movement, receives motor innervation from the nerve.
Function of the Marginal Mandibular Nerve
The primary function of the marginal mandibular nerve is to provide motor innervation to the muscles responsible for the movements of the lower lip and chin. These muscles include the depressor anguli oris, depressor labii inferioris, and mentalis. The coordinated action of these muscles allows for various facial expressions, such as smiling, frowning, and pouting.
In addition to its role in facial expression, the marginal mandibular nerve also plays a crucial role in maintaining facial symmetry. By modulating the position and mobility of the lower lip, the nerve helps to ensure that both sides of the face are balanced and harmonious. Any disruption or injury to the nerve can lead to asymmetry and affect the overall appearance of the face.
Understanding the function of the marginal mandibular nerve is essential for healthcare professionals, particularly those involved in facial surgery and cosmetic procedures. Knowledge of the nerve’s role in controlling the lower lip and chin allows for precise surgical planning and helps to minimize the risk of complications. It also enables healthcare providers to address any issues related to the nerve, such as paralysis or weakness, and develop appropriate treatment strategies.
In conclusion, the marginal mandibular nerve is a vital component of the facial nerve system, responsible for providing motor innervation to the muscles of the lower lip and chin. Its anatomy and function are complex, with variations in its course and important landmarks along its path. Understanding the intricate details of this nerve is crucial for accurate examination, surgical procedures, and maintaining facial symmetry.
Preparing for the Examination
Preparing for a nerve examination requires careful attention to detail and the gathering of necessary equipment. The examination room should be well-lit, providing optimal visibility for the healthcare professional. Adequate magnification is also essential to ensure a comprehensive assessment of the nerves. This combination of lighting and magnification allows for accurate detection of any abnormalities or signs of nerve dysfunction.
Necessary Equipment for Checking the Nerve
When it comes to checking the nerve, having the right tools at hand is crucial. One of the essential tools is a tongue depressor, which helps to gently hold the tongue down, allowing for a clear view of the nerves in the oral cavity. A cotton-tipped applicator is another indispensable tool, enabling the healthcare professional to apply gentle pressure to specific areas, assessing the patient’s response. Lastly, a neurologic reflex hammer is necessary to test the reflexes and evaluate the nerve pathways.
Each of these tools plays a vital role in facilitating a comprehensive nerve examination. The tongue depressor and cotton-tipped applicator allow for precise manipulation and assessment, while the neurologic reflex hammer provides valuable insights into the functioning of the nerves.
Patient Preparation Guidelines
Ensuring that the patient is adequately prepared for the examination is of utmost importance. Educating the patient about the procedure and obtaining their informed consent are essential steps in establishing trust and cooperation. It is crucial to address any concerns or questions the patient may have, as this helps to alleviate anxiety and create a comfortable environment.
One aspect of patient preparation that often goes unnoticed is advising the patient to refrain from consuming stimulants such as caffeine or nicotine before the examination. These substances can have an impact on the patient’s ability to remain still during the examination, potentially affecting the accuracy of the results. By informing the patient about this, healthcare professionals can ensure that the examination is conducted under optimal conditions.
Furthermore, ensuring the patient’s relaxation and comfort throughout the entire process is paramount. Creating a calm and soothing environment can help alleviate any tension or apprehension the patient may be feeling. This can be achieved by providing a comfortable examination table or chair, playing soft background music, or using aromatherapy techniques to promote relaxation.
By following these patient preparation guidelines, healthcare professionals can enhance the overall experience for the patient and increase the likelihood of a successful examination. Patient comfort and cooperation are crucial in obtaining accurate results and providing the best possible care.
Step-by-Step Procedure to Check the Marginal Mandibular Nerve
Initial Assessment
Before commencing the examination, perform a thorough initial assessment to establish baseline findings. This initial assessment is crucial in understanding the patient’s facial characteristics and any potential abnormalities. Observe the patient’s facial symmetry at rest, noting any apparent asymmetry, drooping of the lower lip, or abnormal movement patterns. Take note of any visible signs that may indicate issues with the marginal mandibular nerve.
In addition to visual observation, it is important to assess the patient’s sensory perception. Gently touch the lower lip and chin, and ask the patient to report any numbness or tingling sensations. This will help determine if there are any sensory abnormalities associated with the marginal mandibular nerve.
Performing the Examination
Once the initial assessment is complete, you can proceed with the examination of the marginal mandibular nerve. Begin by asking the patient to mimic various facial expressions, such as a smile or pout. Carefully observe the movement of the lower lip, paying close attention to any asymmetry or weakness. This will provide valuable information about the functionality of the marginal mandibular nerve.
To further assess the nerve’s function, you can use a tongue depressor to gently depress the lower lip. As you do this, observe for any deviation or asymmetry in the movement of the lip. Any abnormalities in the lip’s response may indicate issues with the marginal mandibular nerve.
Another technique to evaluate the nerve is by applying light pressure on the chin with a cotton-tipped applicator. Observe the patient’s response and assess for any asymmetrical movements. This will help determine if the marginal mandibular nerve is functioning properly.
Throughout the examination, it is essential to maintain clear communication with the patient. Provide gentle instructions and encourage relaxation to ensure accurate assessment of the marginal mandibular nerve. Remember to document any findings and communicate them to the appropriate healthcare professionals for further evaluation if necessary.
Interpreting the Results
After conducting a thorough examination, it is important to understand and interpret the results accurately. This will help in determining the presence of any abnormalities or potential issues related to the marginal mandibular nerve. By analyzing the findings, healthcare professionals can provide appropriate guidance and treatment options to the patients.
Normal Findings and What They Mean
In a normal examination, the marginal mandibular nerve should provide symmetrical and coordinated movements of the lower lip and chin. This means that the patient should be able to fully mimic facial expressions without any noticeable asymmetry or weakness. The nerve functions optimally, allowing for smooth and synchronized movements.
In addition to motor function, sensory perception is also an important aspect to consider. In a normal examination, the patient should report no numbness or tingling upon gentle stimulation. This indicates that the nerve is effectively transmitting sensory information, ensuring normal sensation in the lower lip and chin area.
Abnormal Findings and Potential Causes
Abnormal findings in the examination may indicate a dysfunction or injury to the marginal mandibular nerve. These findings should be carefully assessed and further investigated to determine the underlying cause and appropriate treatment plan.
Facial asymmetry, such as drooping of the lower lip, weak or unequal movement patterns, or a lack of coordination, may be indicative of nerve damage. These symptoms can significantly impact the patient’s ability to express emotions and perform daily activities involving the mouth and lower face.
There are various potential causes for abnormal findings in the examination. Trauma, such as a direct blow to the face or a motor vehicle accident, can result in nerve damage. Infections, such as viral or bacterial infections affecting the facial nerves, can also lead to abnormal findings. Additionally, tumors or growths in the area can compress or damage the marginal mandibular nerve, causing dysfunction.
It is important to consider iatrogenic factors as well, which refer to nerve damage caused by medical procedures. Surgical procedures in the area, such as facial cosmetic surgeries or dental procedures, can inadvertently affect the marginal mandibular nerve, leading to abnormal examination findings.
However, it is crucial to note that further investigation is necessary to confirm any suspicions. A consultation with a healthcare professional, such as a neurologist or an otolaryngologist, is strongly recommended. These specialists can conduct additional tests, such as electromyography or imaging studies, to provide a more accurate diagnosis and develop an appropriate treatment plan.
Overall, interpreting the results of a marginal mandibular nerve examination requires a comprehensive understanding of normal and abnormal findings. By carefully analyzing the patient’s symptoms and medical history, healthcare professionals can determine the presence of any dysfunction or injury to the nerve and provide appropriate care and support to the patient.
Safety Measures and Precautions
The examination of the marginal mandibular nerve is generally safe and non-invasive. However, as with any medical procedure, there are minimal risks involved. These may include mild discomfort, transient bruising, or allergic reactions to certain examination tools. It is essential to take necessary precautions and ensure proper sterilization and maintenance of equipment to minimize any potential complications.
When it comes to ensuring the safety of patients during the examination of the marginal mandibular nerve, healthcare professionals should prioritize aseptic techniques. Aseptic techniques refer to the practices that prevent the introduction of harmful microorganisms into a patient’s body. By following these techniques, healthcare professionals can significantly reduce the risk of infection and other complications.
One of the key aspects of aseptic techniques is the use of single-use or properly sterilized examination tools. These tools, such as cotton-tipped applicators, should be handled with care and disposed of appropriately after each use. By using disposable tools, the risk of cross-contamination between patients is minimized, ensuring a clean and safe environment for everyone involved.
In addition to proper tool sterilization, healthcare professionals should also prioritize effective communication with the patient. Establishing a comfortable and cooperative environment is crucial in preventing complications during the examination. By explaining the procedure to the patient, addressing any concerns or questions they may have, and ensuring their understanding and consent, healthcare professionals can help alleviate anxiety and promote a smoother examination process.
Furthermore, healthcare professionals should also consider the patient’s medical history and any known allergies. By being aware of any potential allergic reactions, they can take appropriate measures to avoid using examination tools or substances that may cause harm. This includes conducting thorough patient interviews and reviewing medical records to gather relevant information.
Overall, the examination of the marginal mandibular nerve is a safe procedure when proper safety measures and precautions are followed. By prioritizing aseptic techniques, utilizing sterilized or single-use tools, and maintaining effective communication with the patient, healthcare professionals can minimize potential complications and ensure a positive experience for the patient.
Post-Examination Follow-Up
Communicating the Results to the Patient
After completing the examination, it is crucial to communicate the results to the patient in a clear and empathetic manner. This step is essential in ensuring that the patient understands their condition and the necessary steps for further evaluation and treatment. Effective communication can help alleviate any anxiety or concerns the patient may have.
When presenting any abnormalities or concerns identified during the examination, it is important to approach the conversation with sensitivity. The patient should be informed about the findings without causing alarm, emphasizing the need for further evaluation by a qualified healthcare professional. This can help the patient understand the importance of seeking appropriate follow-up care and taking necessary actions to address their health concerns.
During the communication process, healthcare professionals should provide the patient with resources and guidance to seek appropriate follow-up care. This may include providing information about specialists or clinics that specialize in the specific condition identified, as well as any support groups or educational materials that can help the patient better understand their condition and available treatment options. By equipping the patient with these resources, healthcare professionals can empower them to take an active role in their healthcare journey.
Next Steps After the Examination
Based on the examination results, the appropriate next steps will vary. It is imperative for healthcare professionals to collaborate with other specialists, such as oral and maxillofacial surgeons or neurologists, to discuss the findings and develop a comprehensive management plan. This interdisciplinary approach ensures that the patient receives the most appropriate and effective care.
Further diagnostic investigations may be necessary to confirm a diagnosis and guide treatment options. These investigations can include imaging studies, such as magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) or computed tomography (CT) scans, which provide detailed images of the affected area. Additionally, nerve conduction tests may be conducted to assess the function of the marginal mandibular nerve and determine the extent of any abnormalities.
Once a diagnosis is confirmed, healthcare professionals can work with the patient to develop an individualized treatment plan. This plan may include a combination of medical interventions, such as medication or physical therapy, as well as lifestyle modifications to manage symptoms and improve overall well-being. Regular follow-up appointments will be scheduled to monitor the patient’s progress and make any necessary adjustments to the treatment plan.
In conclusion, checking the marginal mandibular nerve requires a systematic approach, understanding of anatomical landmarks, and proper patient preparation. By following the step-by-step procedure outlined in this article, healthcare professionals can accurately assess the function of the marginal mandibular nerve and identify any abnormalities. However, it is important to remember that this article serves as a guide and does not substitute consultation with a qualified healthcare professional.